蒙地卡羅模擬(Monte Carlo Simulation)
在介紹蒙地卡羅模擬前,一定要提的就是布朗運動(Brownian Motion, BM),理論介紹內容參考 Option, Futures and Other Derivatives, Ninth Edition, John C. Hull
當一變數符合馬可夫隨機過程(Markov Stochastic Process),平均數為 0 ,變異數為 1 ,則我們稱這段數列符合維納過程,或稱作布朗運動,數學上有兩個性質
性質1: 假設現在有一變量 z,此變量的於一短時間內(△t)變動符合標準常態分配。
$$ \Delta z = \epsilon \sqrt{\Delta t}, \epsilon \backsim \phi(0,1) $$
性質2: 兩期間的變量相互獨立,不互相影響。
簡單來說,當一變量符合上述兩個性質,則稱該變量符合維納過程。而所謂的一般維納過程可以寫成下式
$$ dx = adt + bdz $$
在等號的右手邊為由兩項所組成, $a$ 乘上 $d_t$ 是所謂的飄移項(drift term) ,而 $b$ 乘上維納過程($dz$)則稱為變異項(variance term) 。
介紹完布朗運動後,將變量代換到股價的話,則可以將公式寫成如下
$$ dS = \mu Sdt + \sigma Sdz $$
$$ \frac{dS}{S} = \mu dt + \sigma dz $$
而等號左右同除 S後的第二行,即得到報酬率的概念,如此一來,這模型即為蒙地卡羅模擬,我們能用它來模擬股價路徑,進而求得選擇權價格。
蒙地卡羅模擬程式碼
我們透過模擬m次股價,並將每次拆分為 t/n 期,最後求出每次模擬期末的選擇權價格,接著將其平均並折現。
def Monte_Carlo_Simulations(
c_p: str,
mu: float,
sigma: float,
s: float,
k: float,
r: float,
t: float,
n: int,
m: int,
) -> float:
delta_t = t / n
simulation_results = []
for _ in range(m):
price_path = [s]
for _ in range(n):
random = np.random.standard_normal()
price_path.append(
price_path[-1]*np.exp(
mu*delta_t + sigma*random*delta_t**0.5)
)
simulation_results.append(price_path[-1])
if c_p == 'call':
option_price = sum([max(s - k, 0) for s in simulation_results]) / m
elif c_p == 'put':
option_price = sum([max(k - s, 0) for s in simulation_results]) / m
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong c_p.')
option_price = option_price*np.exp(-r*t)
return option_price
三元樹(Trinomial Tree)
先前介紹的二元樹,認為股價於下一期會有兩種走勢,上升(up)和下降(down),三元樹則是多了一個(middle)的移動,也就是平移不變。
提供書中的圖來給大家參考,真心推薦買一本 Option, Futures and Other Derivatives, Ninth Edition, John C. Hull
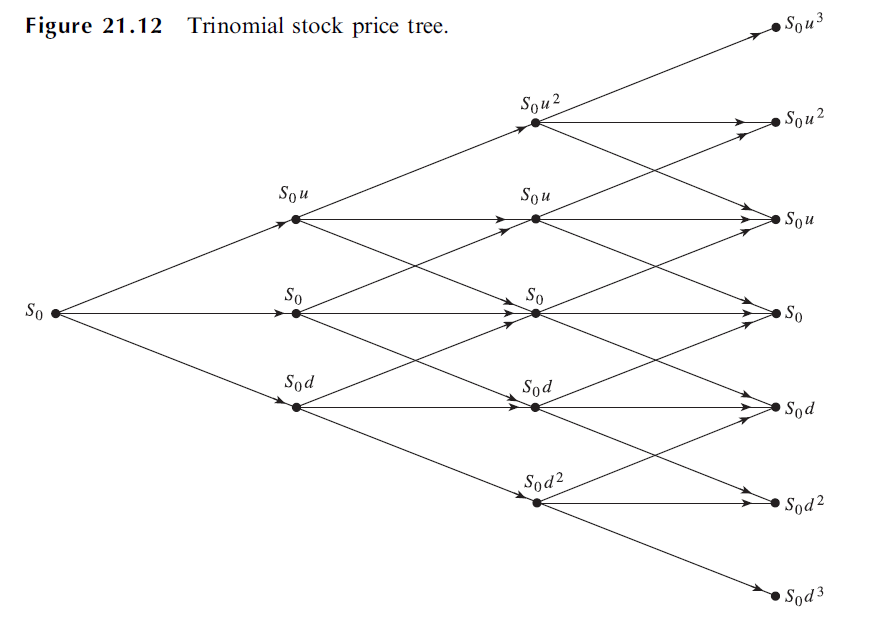
儘管公式上看來複雜許多,但計算上是容易的,除了原本上升和下降的機率外,增加了平移的機率,固定為 66.7%。
$$ u = e^{\sigma \sqrt{3 \Delta t}}, d = 1 / u $$
$$ p_d = -\sqrt{\frac{\Delta t}{12\sigma^2}}(r-q-\frac{\sigma^2}{2}) + \frac{1}{6}$$ $$ p_m = \frac{2}{3} $$ $$ p_u = \sqrt{\frac{\Delta t}{12\sigma^2}}(r-q-\frac{\sigma^2}{2}) + \frac{1}{6} $$
三元樹程式碼
和寫二元樹同樣,三元樹我們也寫歐式的,寫法同樣是先將期末的各種可能價格計算出來後,在將結果(上升、平移、下降)呈上對應的機率並折現,不斷回推後計算出當前的理論價格。
美式最大的差別在於可以提前履約,而如果寫美式選擇權評價除了要將每期的資產價格計算出來之外,美式每期選擇權價格將會是
- 預期資產價格下的選擇權價格
- 下一期結果折現回推的選擇權價格,兩者取最大值。
def trinomial_tree_option_pricing(
c_p: str,
s: float,
k: float,
r: float,
v: float,
q: float,
t: float,
n: int,
) -> float:
"""
Test1:
trinomial_tree_option_pricing(
c_p = 'call', s = 810, k = 800, r = 0.05,
v = 0.2, q = 0.02, t = 6/12, n = 2
)
Output:
51.9569
---
Test2:
trinomial_tree_option_pricing(
c_p = 'put', s = 50, k = 50, r = 0.1,
v = 0.4, q = 0, t = 5/12, n = 5
)
Output:
3.8110
"""
delta_t = t / n
u = np.exp(v*np.sqrt(3*delta_t))
d = 1 / u
p_d = -np.sqrt(delta_t/(12*v**2))*(r-q-v**2/2) + 1/6
p_u = np.sqrt(delta_t/(12*v**2))*(r-q-v**2/2) + 1/6
p_m = 2/3
asset_price = [s*d**(n-i) for i in range(n)] + [s] + [s*u**(i) for i in range(1, n+1)]
if c_p == 'call':
option_price = [max(s - k, 0) for s in asset_price]
elif c_p == 'put':
option_price = [max(k - s, 0) for s in asset_price]
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong c_p.')
option_tree = [[] for _ in range(n)]
option_tree.append(option_price)
for i in range(1, n+1):
last_level = option_tree[n-i+1]
for j in range(2, len(last_level)):
down_price = last_level[j-2]
middle_price = last_level[j-1]
up_price = last_level[j]
option_tree[n-i].append(
np.exp(-r*delta_t)*(up_price*p_u + middle_price*p_m + down_price*p_d)
)
return option_tree[0][0]

