- What is a Stack?
- When and where is a Stack used?
- Complexity
- Example - Brackets
- Leetcode problem
- Reference
What is a Stack?
A stack is a one-ended linear data structure which model a real world stack by having two primarily operations, namely push and pop.
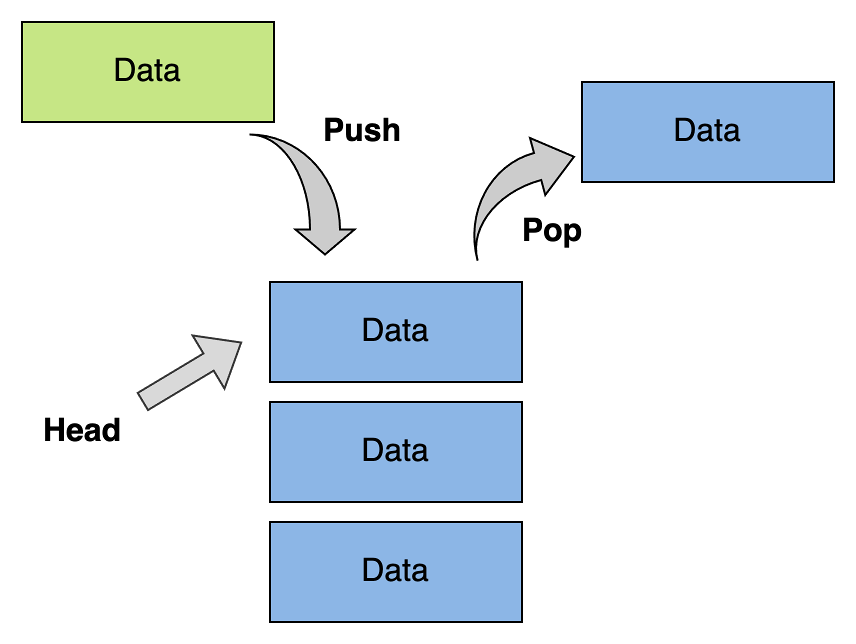
When and where is a Stack used?
- Used by undo mechanism in text editors.
- Used in complier syntax checking for matching brackets and braces.
- Can be used to model pile of books or plates.
- Used behind the scenes to support recursion by keep tracking the previous function calls.
- Can be used to do a Depth First Search(DFS) on a graph.
Complexity
| Action | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Pushing | $O(1)$ |
| Popping | $O(1)$ |
| Peeking | $O(1)$ |
| Searching | $O(n)$ |
| Size | $O(1)$ |
Example - Brackets
Given a string made up of the following brackets: {}()[], determine whether the brackets are properly match.
| String | Result |
|---|---|
[{}] |
Valid |
(()()) |
Valid |
[()]}[ |
Invalid |
Leetcode problem
- If current string is the left side of brackets, then append it into stack.
- If current string is the right side of brackets, then find the correspond left side and check whether the last element in stack is matched.
- Eliminate the pair brackets.
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
n = len(s)
stack = []
mappings = {
')':'(',
'}':'{',
']':'[',
}
for i in range(n):
rev = mappings.get(s[i])
if s[i] in mappings.values():
stack.append(s[i])
else:
if len(stack) == 0 or stack[-1] != rev:
return False
else:
stack.pop()
return len(stack) == 0

